Services
- Static Equipment & Structures (Piping Vibration & Fatigue)
- Acoustic Fatigue Assessment for Blowdown Systems
- Acoustic-Induced Vibration (AIV) Analysis
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Flow-Induced Turbulence (FIT) Analysis
- Flow-Induced Vibration (FIV) Analysis
- Multiphase and Slug Flow Analysis
- Pipe Stress Analysis
- Piping Vibration and Integrity Assessment
- Review & Design Support Services
- Small-Bore Connections (SBC) Assessment
- Structural Vibration and Dynamic Design Analysis
- Subsea Piping Vibration
- Thermal Striping
- Tube Failure Analysis
- Veridian AM
- Veridian VS
- Vibration Inspection Program
- Water Hammer Analysis
- Machinery Analysis
- Bottle Sizing Service
- Compressor Package Engineering
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Foundation Design and Dynamic Analysis
- Fuel Gas Compressor Piping Transient Analysis
- Lateral Vibration Analysis
- Pipe Stress Analysis
- Pulsation & Mechanical Analysis: Reciprocating Compressor
- Pulsation & Mechanical Analysis: Reciprocating Pump
- Pulsation & Mechanical Analysis: Screw Compressor
- Pump RCF Analysis
- Review & Design Support Services
- Shell Transverse Acoustical (STA) Analysis
- Skid Design and Analysis
- Surge Control Design for Centrifugal Compressor Systems
- Torsional Vibration Analysis (TVA)
- Field Engineering & Troubleshooting
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Human Vibration
- Motion Amplification Vibration Analysis
- Noise Troubleshooting
- Performance Assessment (Thermodynamic)
- PostPro – field data processing and analysis
- Structural Vibration Troubleshooting
- Thermal Striping
- Troubleshooting, Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Veridian iDAC
- Vibration Inspection Program
Thermal Striping
High-cycle thermal strain in liquid mixing piping
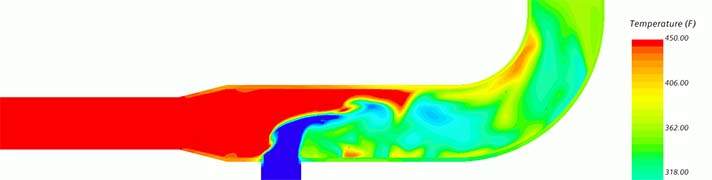
The mixing of different temperature fluids can create eddies of “hot” and “cold” flow. Surface temperature fluctuations will induce dynamic surface strains, which can lead to fatigue failure of piping and components.
Wood brings together detailed computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to predict the fluid mixing and finite element analysis (FEA) modelling to evaluate the transient thermal loads, calculate material strains, and estimate fatigue life. Typical solutions include diffusers and mixing nozzles or selecting improved materials for affected components.
Contents [ hide ]
1 What is thermal striping?
Thermal striping is a complex phenomenon where cold and hot flow streams are mixed at a T-junction piping and generate fast temperature fluctuations at the fluid-wall interface. Consequently, the temperature of the adjoining structural wall surface fluctuates with minimal attenuation, which eventually induces dynamic strains and stresses leading to fatigue failure of piping and components.
Thermal striping and resulting fatigue are the major degradation mechanisms for mechanical components in different industries, including automotive, thermal power plants, nuclear plants, piping in petrochemical plants, oil and gas industry and aerospace industry.
2 What factors affect thermal striping?
The frequency and amplitude of temperature fluctuations are important factors that affect the structural damage under thermal striping. Temperature fluctuations at higher frequencies cannot penetrate the pipe wall while the low-frequency fluctuations result in small stress amplitudes since pipe temperature does not change considerably along with the thickness. Therefore, fluid temperature fluctuation frequencies in the range of 0.1-10 Hz are most problematic for thermal striping.
3 What is thermal fatigue?
Thermal fatigue caused by fluid temperature fluctuations is a high-cycle fatigue phenomenon with low-amplitude thermal loads. It is an interdisciplinary phenomenon that needs different evaluation and studies including fluid dynamics, heat transfer, structural mechanics and fatigue analysis.
4 How can thermal striping be detected and mitigated?
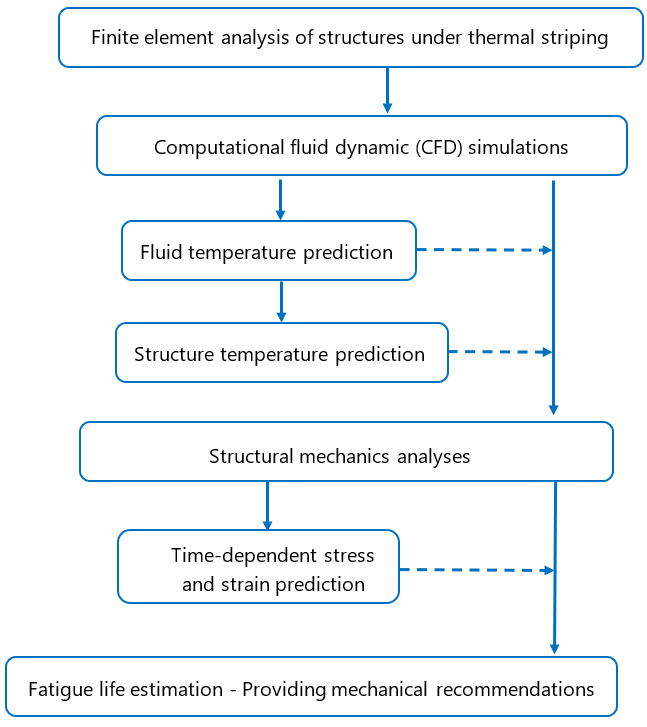
Wood provides a comprehensive finite element analysis of mechanical systems under thermal striping and fatigue by taking three steps:
- The first step is fluid dynamics analysis that is done using computational fluid dynamic (CFD) simulations of turbulently mixed fluids with relatively high Reynolds numbers. This analysis predicts the flow and temperature fluctuations in the system and also provides the frequency and amplitude of oscillations. Temperature distribution on the pipe is then predicted based on the heat transfer coefficient between the fluid and the pipe as well as the heat conductivity of the pipe.
- The second step is the structural mechanics analyses using finite element method (FEM) to predict time-dependent strain and stress values in the pipe wall under thermal loadings predicted previously.
- In the final step, fatigue analysis is completed based on the thermal loads and resultant strain and stress fields obtained in the previous step. The fatigue life of pipe is estimated through post-processing procedures and required mechanical recommendations are provided accordingly to prevent failure.
4.1 Design
During design, Wood can provide process simulation, CFD/FEA modelling, and fatigue analysis.
4.2 Operations
In the field, we can fix thermal striping issues with a root cause analysis (RCA) on failures, field vibration/strain auditing, and CFD/FEA modelling to confirm the presence of thermal striping. Several solutions can be investigated before major mitigations are undertaken.
4.3 Fatigue analysis approach
A summary of the fatigue analysis that Wood takes for structures under thermal striping is illustrated in the following flowchart:
Free webinar
Learn how to select and design vibration control solutions that work – using real-world data and case studies. Register now



