Services
- Static Equipment & Structures (Piping Vibration & Fatigue)
- Acoustic Fatigue Assessment for Blowdown Systems
- Acoustic-Induced Vibration (AIV) Analysis
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Flow-Induced Turbulence (FIT) Analysis
- Flow-Induced Vibration (FIV) Analysis
- Multiphase and Slug Flow Analysis
- Pipe Stress Analysis
- Piping Vibration and Integrity Assessment
- Review & Design Support Services
- Small-Bore Connections (SBC) Assessment
- Structural Vibration and Dynamic Design Analysis
- Subsea Piping Vibration
- Thermal Striping
- Tube Failure Analysis
- Veridian AM
- Veridian VS
- Vibration Inspection Program
- Water Hammer Analysis
- Machinery Analysis
- Bottle Sizing Service
- Compressor Package Engineering
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Foundation Design and Dynamic Analysis
- Fuel Gas Compressor Piping Transient Analysis
- Lateral Vibration Analysis
- Pipe Stress Analysis
- Pulsation & Mechanical Analysis: Reciprocating Compressor
- Pulsation & Mechanical Analysis: Reciprocating Pump
- Pulsation & Mechanical Analysis: Screw Compressor
- Pump RCF Analysis
- Review & Design Support Services
- Shell Transverse Acoustical (STA) Analysis
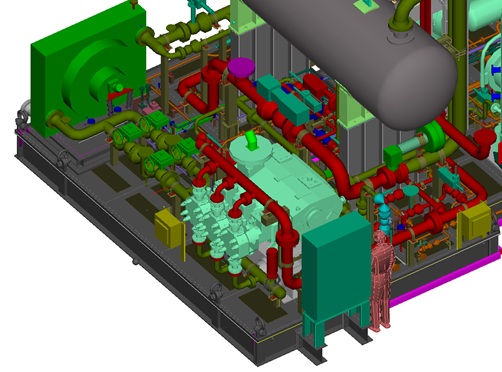
- Skid Design and Analysis
- Surge Control Design for Centrifugal Compressor Systems
- Torsional Vibration Analysis (TVA)
- Field Engineering & Troubleshooting
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Human Vibration
- Motion Amplification Vibration Analysis
- Noise Troubleshooting
- Performance Assessment (Thermodynamic)
- PostPro – field data processing and analysis
- Structural Vibration Troubleshooting
- Thermal Striping
- Troubleshooting, Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Veridian iDAC
- Vibration Inspection Program
Pulsation & Mechanical Analysis: Reciprocating Pump
This analysis includes a pulsation study, a mechanical review, mechanical frequency avoidance analysis, and a forced response analysis (per API 674, API RP 688), if required.
Background
Reciprocating pumps (including diaphragm pumps, plunger pumps, and other positive displacement pumps) are used in many applications, including petroleum production facilities and refineries.
A pulsation and mechanical analysis is often necessary for new or modified reciprocating pumps to avoid typical problems such as:
- Excessive piping vibration and piping failures
- Small-bore attachment failures
- Pressure pulsation-induced cavitation
- Undesired opening of PSVs due to pulsations
- Improper pump valve dynamics leading to poor valve life, and reduced flow capacity
The API 674 pulsation and mechanical analysis is conducted during the design stage. Along with this analysis, it is common to also have a small-bore piping (SBP) analysis, and structural vibration and dynamic design analysis if the pump is to be mounted on steel structures.
Contents [ hide ]
1 Scope
A vibration study includes different design components depending on the risk and application. The standard requirements often include:
- Pulsation and Mechanical Analysis (see 1.1 and 1.2 below)
- Small-Bore Connections (SBC) Assessment
Depending on the application, these studies may be required:
- (Onshore) Foundation Design and Dynamic Analysis
- Pump Pulsation Application Guide (pdf)or contact our application support for assistance.
1.1 Pulsation Analysis (Acoustical Analysis)
This study is also known as a Design Approach 2 (DA2) per API 674 terminology and applies to “medium” risk units per our Application Guide (pdf)
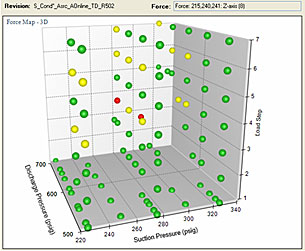 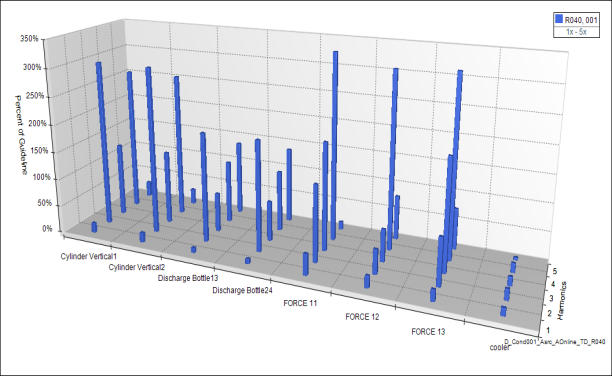 |
| DataMiner™ software analyzes pressure pulsations, forces and other vibration issues – across hundreds of conditions and locations in the piping system. See why DataMiner provide extra value for your projects. Read more |
Features include:
- Operating conditions. An operating condition analysis to assess the pump’s operation across the entire operating envelope. The standard service evaluates up to 20 operating conditions.
- Pulsation levels. An evaluation of the pulsation levels given varying performance of the pump valves. Pulsation levels are drastically influenced by the behaviour of the pump valves
- Upset conditions. Reporting of the effect of upset conditions such as pulsation levels when a pump valve fails, thus deactivating a plunger throw. Vibration and pulsation characteristics are greatly influenced by the number of fluid ends active.
- Pulsations and other dynamic loads. Wood will assess pulsations and other dynamic loads for the supplied conditions including pressures, temperatures, composition, and speed ranges.
- Pressure pulsations. Wood will assess the magnitude of pressure pulsations and pulsation-induced shaking forces in the piping system using its MAPAK simulation software. Time Domain acoustic simulation is recommended for accurate pulsation analysis, compared to the older Frequency Domain approach. More on pulsation software
- Pulsation control. Pulsations are controlled using acoustic filters, gas charged dampeners, commercially available pulsation control vessels, orifice plates, resonators and/or piping modifications. Pulsations (pressure and forces) are controlled to API 674 (most recent edition) or other field proven guidelines.
- Pressure drop. As a standard feature Wood will assess static and total pressure drop. Total pressure drop includes dynamic pressure drop losses.
- Piping restraint or mechanical review. This includes an evaluation of pipe support locations using charts, empirical calculations, and good engineering design practices.
- Results and reporting. Wood’s DataMiner™ software tool and reporting approach provides valuable information on the pump’s pulsation predictions and performance.
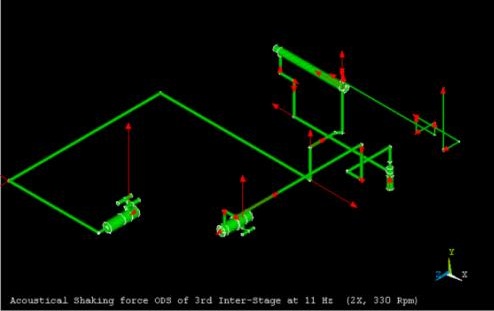 |
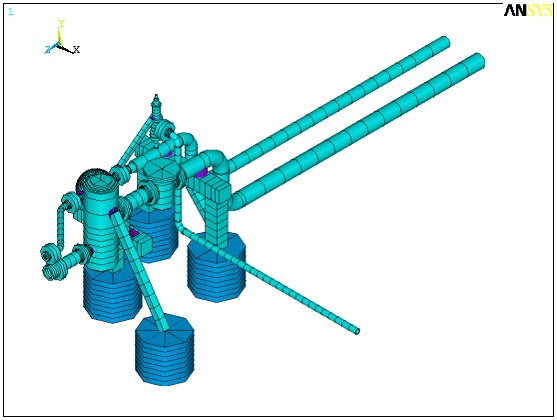
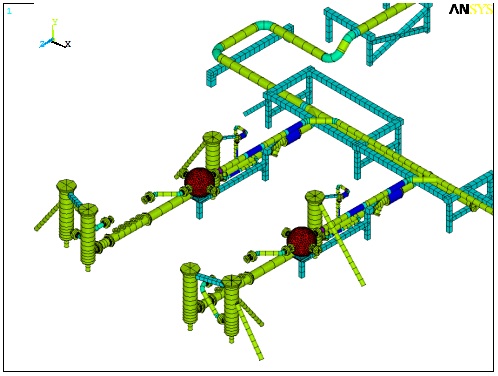
| This acoustic model of the piping system is used to determine pulsation pressure and unbalanced forces at all operating conditions and locations in the system. This example illustrates the 3rd interstage system. The red arrows represent the magnitude of the forces. |
| Reduction in pulsation forces | |
|---|---|
As found Piping System (No Pulsation Study) | After Wood Pulsation Study (Using Time Domain Solver) |
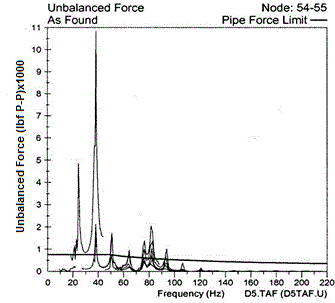 | 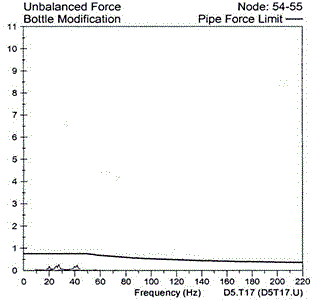 |
Forces above 11,000 lbf | Forces below 200 lbf, well below guideline |
1.2 Mechanical Analysis
This study is part of a Design Approach 2 (DA2) per API 674 terminology and includes the following features:
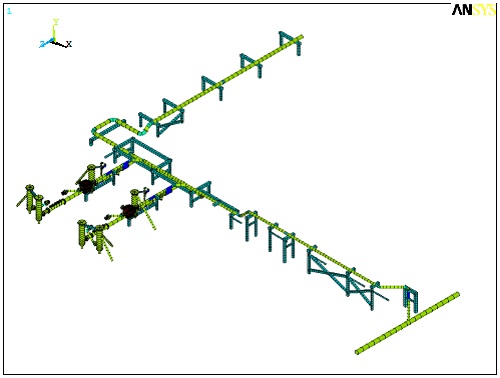
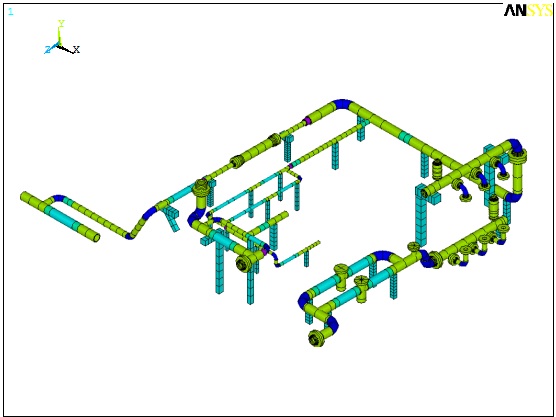
- Finite element (FE) model. Wood will quickly generate an accurate FE model of the pump, vessels, piping system, and key areas of the skid (if applicable). For even more accurate results, a detailed model of the pump frame and/or the full skid and foundation can be included in the model. Wood uses ANSYS for all FE models to ensure accurate results. Some piping finite element analysis (FEA) programs are not recommended for this application.
- Accuracy. Complex geometries are accurately modelled using shell or solid elements. Rotational inertias are included.
- Mechanical natural frequencies (MNFs). The MNFs and mode shapes are determined for the key components in the system, with results published in the report.
- Frequency avoidance. MNFs shall have a 20% margin of separation above 1X plunger passing run speeds, and 20% away from other orders that have significant forces.
- Results and reporting. A detailed report is provided, summarizing recommendations and mechanical results.
A mechanical analysis requires accurate FE models of the pump piping system to determine MNFs and avoid resonance. Models are also used in Forced Response Analysis (option below) to determine vibration and stress amplitudes. Field experience and measurements are required to accurately define boundary conditions, dynamic forces, and practical recommendations to avoid problems.
1.3 Options
 |
 |
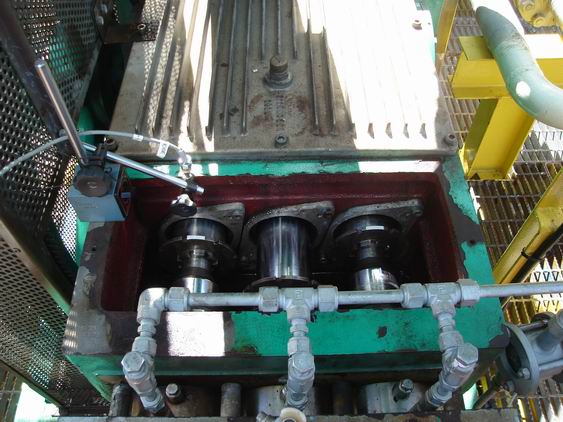 |
The following are commonly required options:
- Small-bore connections (SBC). Wood provides a range of services to design, analyze and test SBC, depending on the application and customer’s risk tolerance. Small-Bore Connections (SBC) Assessment
- Additional operating conditions. For some applications defining 20 operating points (included in the standard study) will not sufficiently cover the range of operating conditions and load steps to ensure all potential pulsation and vibration problem areas are evaluated. Wood can provide assistance in defining the recommended number of conditions to analyze.
- Forced Response Analysis. This analysis is recommended when frequency avoidance recommendations cannot be achieved or implemented. The study includes all significant pump forces (including fluid stretch forces, pulsation forces, and moments and couples) and will evaluate vibration and stress to API 674 and industry guidelines. There are two locations where this option is conducted:
- Pump manifold system - analysis of the dampeners and piping around the pump frame; and
- Piping away from the manifold - recommended when the pulsation force guideline cannot be met, or the Frequency Avoidance Analysis recommendations cannot be implemented.
- Off-skid or station piping. Wood will assess pulsations in piping away from the pump package (if information is available). This added level of analysis is valuable when coolers and/or scrubbers are located away from the pump package, or when pulsations need to be analyzed in the headers and plant piping system.
- Multi-unit Analysis (interaction between units). When multiple pumps are connected together in series or parallel, Wood will evaluate pulsations in headers and plant piping system including interaction between units.
Water hammer analysis, also known as a transient surge analysis for liquid systems, is another optional study that is sometimes required when reciprocating pump and piping systems are affected by transient events such as power outages, valve swings, check valve slam, and other causes. Some operators require an investigation of transients in the system to ensure integrity under upset conditions. See Water Hammer Analysis
2 Wood Advantages
Wood is a global leader in pulsation analysis because of these unique factors:
- We pioneered the development of digital acoustic simulation in the 1970s
- Every year Wood makes significant investments in acoustic simulation tools and field based verification to ensure its MAPAK software is world class (Time Domain-based simulation includes nonlinear fluid dynamics and time-varying boundary conditions, an important feature for modeling higher frequency acoustics and not available with commercially available software used by small firm)
- More standard features offered such as improved performance analysis, more accurate boundary conditions, and improved analysis of off-skid piping
- Better quality control and project management expertise due to focus on quality, technical reviews, and effective client communication to yield a more successful project
- Responsive application advice and ongoing customer service
- Studies compliant with API 618
- Timely and practical recommendations
- Full-time field engineering team to assist with start-up checks or onsite support on a global basis
- Field-verified pulsation and mechanical vibration modeling techniques [note: other firms lack full-time field engineers to provide necessary field input and model verification into their design process, so only theoretical results are provided]
- Local support by experts located in the US, Canada, Malaysia, China, Australia, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and the UK
- Fully integrated vibration solution offered that includes design and field support of compressors, pumps, and piping to ensure your reliability and integrity management requirements are met
- Involved with (and leads) industry research projects for the Gas Machinery Research Council (GMRC) resulting in superior knowledge and expertise
- Active member in API and GMRC vibration task force committees
3 Client Benefits
As the global market leader in pulsation design services, Wood is able to offer a number of unique services and features including accurate pulsation and mechanical analysis that benefit the owner. These benefits include higher system reliability, minimized pressure drop and performance losses, faster turnaround in the design, optimized vessel sizes, and lower overall costs. Other benefits include:
- Pulsation forces controlled throughout the piping system
- Piping and vessel vibration minimized
- Complete range of operating conditions evaluated
- Recommendations provided that represent a balance of all competing requirements (pulsation control, added pressure drop, mechanical constraints, and practical implementation)
- Effective reporting and analysis for useful field analysis and monitoring
4 Related Information
The pulsation and mechanical analysis for reciprocating pumps is quite similar to the analysis offered for reciprocating compressors. For explanation of the issues, please refer our Knowledge Center for videos and articles relating to these subjects.
 |
 |
 |
- Webinar recording: How to select the right dampener for a reciprocating pump system
- Specification for purchasing a vibration design study (pdf)
- Tips for Managing a successful vibration project
- Recommended Guidelines and References
- Pipe clamps for vibratory service
Pump articles:
- Taking the plunge – vibration-induced cracks in plunger pump piping (Hydrocarben Engineering)
- Poor Pump Design Can Limit Operations (pdf)
- Far Reaching Effects of Inadequate Pulsation Control (pdf)
- Reciprocating Pump Design Flaws Shut Down Oil Platform (pdf)
- Integrity of Pulsation Dampeners in Liquid Systems (pdf)
- Incorrect Valve Selection on Plunger Pumps (pdf)
Video examples:
5 Related Services
Common studies that may be coordinated with the pulsation/mechanical analysis:
- Small-Bore Connections (SBC) Assessment
- Torsional Vibration Analysis
- Pipe Stress Analysis (Thermal Flexibility Study)
- Skid Design and Analysis
- Foundation Design and Dynamic Analysis
- Water Hammer Analysis
6 Keywords
- API 674 pulsation study
- Acoustic study
- Dampeners
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
More Info
Webinar: Pump it up, damp it down • Pump Vibration Examples (Video) • Pulsations in Suction Piping (Reciprocating Pump) (Video) •
Free webinar
Learn how to select and design vibration control solutions that work – using real-world data and case studies. Register now



